
Troy J. Bassett, “‘More than a Bookseller’: Iredale’s Library as the Center of Provincial Literary Life”
Andrew Iredale welcomed Her Royal Highness Princess Victoria and her cousins to his library in Toquay, Devon on 1 September 1898 where the group bought books and photographs. Founded by Iredale in 1872, Iredale’s Library became the “centre of literary life” in the seaside resort community well into the twentieth century. This article considers the circulating library’s role in the community: in addition to selling and lending books, the library served as a place for public and private meetings, third-party business transactions, and interpersonal networking. As the history of Iredale’s Library illustrates, provincial circulating libraries played a vital role in communities well beyond their money-making operations.

Lara Kriegel, “On the Death—and Life—of Florence Nightingale, August 1910”
This essay examines the death, and the life, of Florence Nightingale, the great nursing heroine of the Crimean War. An eminent Victorian, Nightingale passed away at the ripe old age of ninety in 1910, at a time when Britain was witnessing great internal strife and facing looming international tension. By that moment, the Crimean War was a thing of the distant past. Even so, Nightingale’s death served as a national tonic. It allowed mourners to rekindle the myths of Nightingale’s lifetime that had unified a ravaged nation in the wake of the Crimean War. Nightingale’s most important reforming efforts, which included nursing education, army improvement, and sanitary reform, both in Britain and in India, would postdate the Crimean War. However, the image of a young Nightingale ministering to the troops in the Crimea would remain the dominant one, not just in her life, but at her death as well. As it assesses the death and life of Nightingale, this essay focuses on two moments of celebrity and mythmaking in the long career of the heroine: the making of her legend in the Crimea and its resurrection at her death. It follows earlier literature, both generated during the nineteenth century and written by those who study it, establishing Nightingale as the avatar of Victorian womanhood. Accordingly, it seeks to understand Nightingale’s passing as a belated death knell to the Victorian age.

Frederick Burwick, “18 June 1815: The Battle of Waterloo and the Literary Response”
Although Europe had celebrated the end of the Napoleonic Wars with the defeat of the French armies and the abdication of the emperor on 11 April 1814, Napoleon escaped and again rallied his troops against the British and Prussian armies. His defeat at Waterloo on 18 June 1815 was the final battle with heavy losses on all sides. The extensive response in the British press was unprecedented. In addition to several military reports of the battle, many civilian eye-witness narratives also appeared. Memoirs, histories, and biographies added to the prose accounts. With contributions from Lord Byron, Sir Walter Scott, Robert Southey, William Wordsworth, and many minor authors, the poetry included both celebrations of the victory and lamentations over the loss of lives. Theatres, too, brought forth numerous spectacles and melodrama. Londoners were also treated to several exhibitions and panorama displaying scenes from the battle (Favret 8-12).

Marjorie Stone, “The ‘Advent’ of Aurora Leigh: Critical Myths and Periodical Debates”
Released by Chapman and Hall on 15 November 1856, Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s Aurora Leigh—a verse-novel and modern epic—set off literary, social, and political reverberations in Britain, North America, and Europe up to the end of the century. “The advent of ‘Aurora Leigh’ can never be forgotten by any lover of poetry who was old enough at the time to read it,” Algernon Charles Swinburne recalled in 1898. By 1900, Aurora Leigh—among much else the first extended poetical portrait of the professional woman writer in English literature—had appeared in more than twenty editions in England and as many in America. Given its innovative, generically mixed form and its controversial contemporary subject matter, it figured in debates over poetry and poetics, the nature of the realist novel, class divisions and social reform, women’s rights, religion, and the politics of nations. Contrary to the critical legend that Aurora Leigh was greeted by an “avalanche of negative reviews,” responses to it were diverse, shaped by periodical competition and differing print-culture, artistic, political, national and religious contexts. This essay surveys seldom-cited notices in the transatlantic daily and weekly press, analyzes critical debates on Aurora Leigh in the major British periodicals, and charts differing patterns in its American and European as compared to its British reception in the years immediately following its publication. It also indicates at points how debates over Aurora Leigh were intertwined with debates in the visual arts associated with the paintings of J. M. W. Turner and the Pre-Raphaelites.

Tom Mole, “Romantic Memorials in the Victorian City: The Inauguration of the ‘Blue Plaque’ Scheme, 1868”
The ‘Blue Plaque’ scheme, which places memorial tablets on houses in London once occupied by distinguished people, was inaugurated in 1868, when the Royal Society of Arts placed the first plaque on the house in Holles Street (off Oxford Street) where Lord Byron was born. This was the first of many plaques: at least 33 were in place by the end of the century, with more planned. The distinctive blue circular design was adopted in 1901 and the scheme continues to operate today under the management of English Heritage. This essay argues that the scheme drew on key Romantic ideas about commemorative practice, expressed by William Godwin, William Wordsworth and Samuel Rogers, as well as memorialising Romantic authors. It suggests that the “Blue Plaques” should be read in the context of a number of pantheonic initiatives undertaken during the period of the Reform agitation, which aimed to promote cultural consensus in the present, by creating consensus about the noteworthy individuals of the past.

Ellen Crowell, “Oscar Wilde’s Tomb: Silence and the Aesthetics of Queer Memorial”
This entry looks at how, in the aftermath of Oscar Wilde’s death, those individuals closest to the writer sought a suitable funerary monument in memorial. I first explore the interpersonal and aesthetic politics that informed the choice of Jacob Epstein as the tomb’s commissioned sculptor, and how that choice must be understood as integral to how we remember Wilde today. Noting how profoundly the aesthetics of funerary sculpture are in dialogue with both literary and queer history, this essay also briefly imagines how an alternate monument adorning Wilde’s tomb might have differently configured that dialogue. By comparing Epstein’s tomb with the radically different aesthetics that guide a “rejected” design, this one by the writer’s close artistic collaborator and friend Charles Ricketts, this essay considers how aesthetics have shaped twentieth and twenty-first century approaches to queer memory, mourning, and modernity.
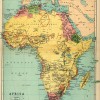
Dane Kennedy, “The Search for the Nile”
This essay examines the social and cultural contexts that informed British explorers’ efforts to discover the source of the Nile. It highlights the relationship of these expeditions to existing systems of trade and power in East Africa, British imperial interests in the region, and the development of a celebrity culture in Britain.

Matthew Rubery, “On Henry Morton Stanley’s Search for Dr. Livingstone, 1871-72”
The meeting between Henry Morton Stanley and Dr. David Livingstone in Africa was one of the most sensational news stories of the nineteenth century. Stanley’s greeting, “Dr. Livingstone, I presume?” is still a well known phrase. The Scottish missionary had been out of contact for several years when an American newspaper sent its correspondent to search for him. The meeting turned public attention to the African slave trade and was a pivotal moment in the relationship among the United States, Europe, and Africa.
